Table of Contents
ToggleEver wondered how our understanding of life has evolved? Well, life science museums are the living libraries of evolution, showcasing the journey of life on Earth in ways that can be mind-blowing (and sometimes a bit weird). From dinosaur fossils that make you question how life used to look, to the tiniest microorganisms that tell stories of survival and adaptation, these museums have it all. Not only do they offer a glimpse into the history of life, but they also educate us on how nature has shaped everything around us. So strap in as we dive deep into the intriguing realm of life science museums and uncover their evolutionary tale.
Historical Overview of Life Science Museums

Life science museums have a rich and varied history, dating back to the very first natural history exhibits created in the 19th century. Initially, these museums were merely collections of specimens gathered by explorers and scientists, often organized haphazardly. Over decades, as our understanding of biology and ecology grew, so too did the sophistication of these institutions.
In the early days, collections were mostly driven by curiosity, with exhibits often showcasing whatever was found interesting or exotic. The British Museum, for instance, established one of the first natural history exhibitions in the late 1700s. This transformed the idea of museums from cabinets of curiosities into organized spaces for learning.
Fast forward to the 20th century, the rise of evolutionary biology prompted a shift in how museums presented their collections. As scientists like Charles Darwin and Gregor Mendel laid the groundwork for modern biology, museums began to display not just specimens but also the stories of how species evolved over time. The focus on evolution brought a paradigm shift in museum curation, emphasizing context and interrelations among different life forms.
Importance of Evolution in Life Science Museums
The concept of evolution is the cornerstone of biological science, and in life science museums, it serves as a foundational narrative that connects all living organisms. By showcasing the evolutionary processes that have shaped life on Earth, these institutions not only educate people about biology but also illuminate our place within the universe.
Understanding evolution allows visitors to grasp the interconnectedness of life: it inspires a sense of curiosity about how species adapt to their environments. This knowledge is crucial as it influences conservation efforts and fosters awareness about endangered species’ fates. Life science museums play an indispensable role in sharing this information, promoting active engagement with critical topics like biodiversity, natural selection, and ecological balance.
Also, evolution-driven exhibits stimulate a sense of wonder and intrigue. They encourage visitors to ask questions like: How did we get here? What forces shaped this organism today? This exploration enhances the learning experience and ignites a passion for science.
Key Features of Modern Life Science Museums
Life science museums have evolved alongside advances in technology and science. Today, they boast several key features that enhance the visitor experience and deepen their understanding of evolution.
Exhibits That Highlight Evolution
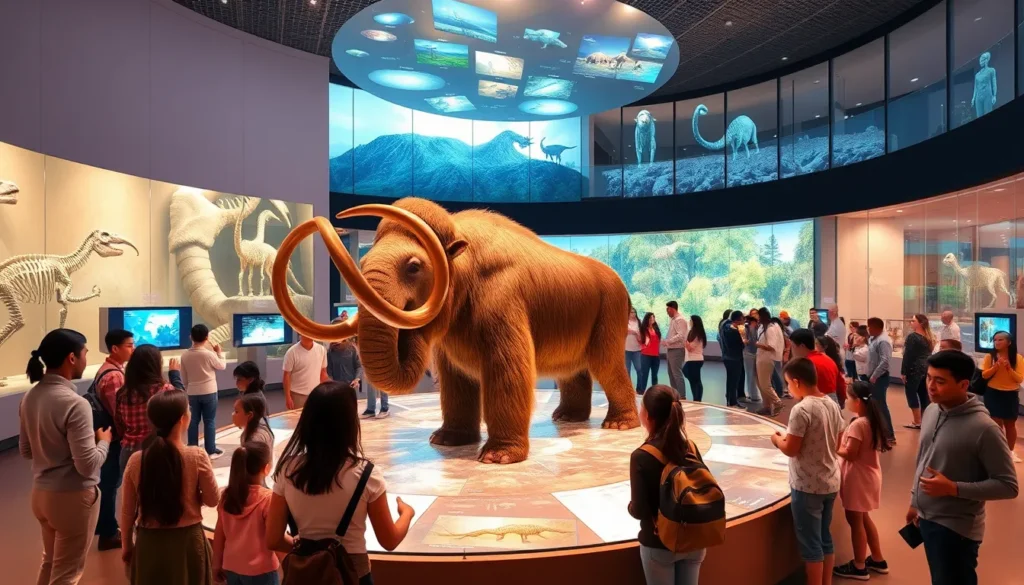
Modern exhibits focus on the storytelling aspect of evolution, providing narrative arcs that connect various species and environments. Interactive displays allow visitors to engage with the material more deeply. For instance, multi-sensory environments replicate prehistoric ecosystems where patrons can experience the sights and sounds of ancient worlds.
Also, many museums use immersive techniques, such as augmented and virtual reality, to bring extinct species to life. Imagine standing beside a lifelike hologram of a woolly mammoth. These advances make evolutionary concepts accessible and memorable, breaking down the often complex scientific terminology.
Interactive and Educational Experiences
Interactive experiences are crucial in modern life science museums. These include hands-on activities like fossil digs or genetic simulations that allow visitors to role-play as scientists. Education programs for schools often involve workshops that emphasize critical thinking about evolution and ecological issues.
Also, modern museums focus on accessibility and inclusivity, ensuring that all visitors, regardless of age or ability, can engage with the exhibits. This commitment to diverse learning experiences makes evolution and life sciences more appealing to wider audiences.
Case Studies of Notable Life Science Museums
Several life science museums stand out as paragons in exhibiting the evolution of life.
The American Museum of Natural History in New York is one such institution. Its vast collection includes a dedicated Hall of Dinosaurs that showcases life forms from millions of years ago, designed meticulously to spotlight evolutionary principles. The museum engages visitors with interactive displays that reveal how paleontologists piece together the past, making evolution tangible and fascinating.
Another noteworthy example is the Field Museum in Chicago, home to the famous Sue, the largest T-rex ever discovered. Beyond its dinosaur exhibits, the Field Museum showcases extensive biodiversity showcases, illustrating the connections between environments, species, and evolutionary adaptations.
Finally, the Natural History Museum in London provides visitors a chronological journey through time with its exhibits, from early life forms to mammals. This historical trajectory celebrates both the science of evolution and its artistic representations, making the biological narrative accessible to all.
Future Trends in Life Science Museums
As technology continues to evolve, so too will life science museums. Future trends indicate a shift toward integrating artificial intelligence and more sophisticated interactive technologies. These innovations promise deeper engagement through personalized experiences. Imagine a museum visit where AI could curate a tour based on your interests, offering insights tailored just for you.
Also, there’s a growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental education within these institutions. Future exhibits will likely focus increasingly on climate change and its impact on biodiversity, urging visitors to participate in conservation efforts.
Collaboration with universities and research institutions will also play a significant role. By becoming hubs for ongoing scientific discourse, museums can remain not only repositories of knowledge but also active contributors to the scientific community’s ongoing research and discussions.